

本文主要介绍了实验中所用的工作电极为在Si(100)上磁控溅射100-200nm厚的Au,其制备流程以及对实验用到的椭偏仪及在位监控实验过程进行介绍。
展示全部 
椭偏仪在位表征电化学沉积的系统搭建(十一)- 工作电极的制备与椭偏仪在位监控
2.1工作电极的制备
实验中所用的工作电极为在Si(100)上磁控溅射100-200nm厚的Au,其制备流程如下:
(1)清洗
由于在生产保存与运输的过程中会使得硅片上残留无机、有机和其他灰尘颗粒污物,其对硅上的镀膜有着较大影响,故而镀膜之前需要对硅片进行清洗。清洗步骤:1.首先在丙酮中用超声清洗仪超声5-10分钟;2.然后用去离子水超声同样的时间;3.接着在酒精中超声清洗;4.zui后再用去离子水超声清洗。在完成以上步骤去除硅片表面的残留污染物后,将其置于鼓风干燥箱干燥即可。
(2)磁控溅射
由于金的晶格常数和硅的晶格常数存在较高的不匹配度,所以需要在硅片上镀一层Ta作过渡金属层增加薄膜之间的附着力。操作步骤:首先,将处理好的硅片放在样品托上,靶材Ta和靶材金均放在直流靶上,关闭腔体进行抽真空,使真空度达到3×10-5Pa;然后打开氩气使腔体得工作压强是0.5Pa,接着开启直流电源,在可以观察到起辉后,于室温下进行溅射。首先在磁控溅射功率70W、氩气流速为35sccm条件下 溅射10nm的Ta层作为过渡层,然后在磁控溅射功率30W、氩气流速为25sccm条件下溅射生长100nm的金层作为该实验的基底。
2.2椭偏仪在位监控
2.2.1椭偏仪
图2-1是实验用的椭偏仪测试装置部分的实物图,其型号是Ellip-SR-I。可以看到该部分由基座、样品台、入射臂、出射臂探测器和角度盘组成。其中角度盘的精度是5°,即入射角度的变化是以5°为单位进行调节的,其调节范围在0-90°。如图2-1所示,为了保证垂直入射出射,样品台的高度可以进行调节,此外整个样品台面还可以在竖直方向上进行。当进行样品测试时,第1步就是进出准直的调节,即使样品测试面在水平,当入射光垂直入射时可以垂直反射。
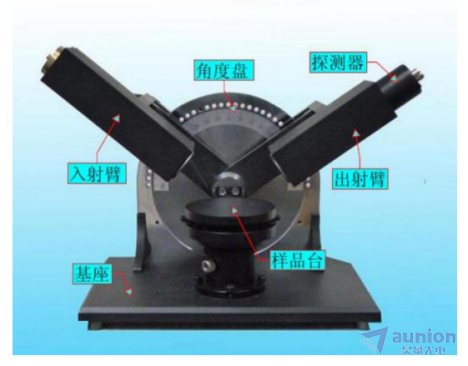
图2-1椭偏仪实物图
2.2.2在位监控
1、Pb溶液体系
在进行不同浓度溶液:5/10/15/20mMPb(CH3COO)2和1MCH3COONa混合溶液的实验,Pb薄膜的沉积实验用的是10mMPb(CH3COO)2和1MCH3COONa混合溶液。该混合溶液透明,但是由于CH3COO-的存在,溶液体系不稳定性,每次实验时都需要即时配制溶液。
2、Cu2O薄膜监控
进行Cu2O薄膜沉积时用的是0.02MCu(CH3COO)2,0.1MCH3COONa混合溶液,该溶液是浅蓝色的,同样存在不稳定性,实验都需要重新配制。
椭偏仪进行Cu2O薄膜监控示意图2-2所示,沉积的装置放在椭偏仪的样品台上,在电化学沉积的同时进行椭偏仪测试,即可实现薄膜沉积的在位监测。
实验中根据设计的电解池,使用CHI-660D电化学工作站设备采用恒流进行电化学沉积Cu2O薄膜,对沉积电流及沉积时间等参数的调节来调控Cu2O薄膜的生长。在进行电化学沉积过程中同时进行椭偏仪的监测,第1组实验是准在位测试,即每沉积180s后进行一次300nm到800nm的椭偏测试,测试的时间点分别是0s、180s、360s、540s、900s及1080s。第二组实验是连续沉积1080s,在这期间同时进行椭偏测试,该组测试椭偏仪取点时间大约是13s每个点。
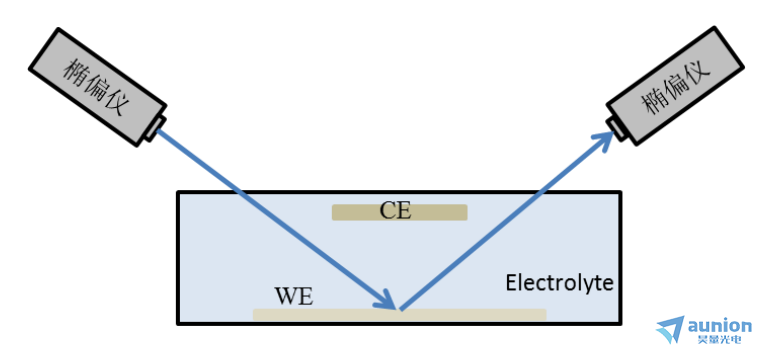
图2-2椭偏仪在位监测示意图
了解更多椭偏仪详情,请访问上海昊量光电的官方网页:
https://www.auniontech.com/three-level-56.html
更多详情请联系昊量光电/欢迎直接联系昊量光电
关于昊量光电:
上海昊量光电设备有限公司是光电产品专业代理商,产品包括各类激光器、光电调制器、光学测量设备、光学元件等,涉及应用涵盖了材料加工、光通讯、生物医疗、科学研究、国防、量子光学、生物显微、物联传感、激光制造等;可为客户提供完整的设备安装,培训,硬件开发,软件开发,系统集成等服务。
您可以通过我们昊量光电的官方网站www.auniontech.com了解更多的产品信息,或直接来电咨询4006-888-532。
相关文献:
[1] WONG H S P, FRANK D J, SOLOMON P M et al. Nanoscale cmos[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1999, 87(4): 537-570.
[2] LOSURDO M, HINGERL K. ellipsometry at the nanoscale[M]. Springer Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London. 2013.
[3] DYRE J C. Universal low-temperature ac conductivity of macroscopically disordered nonmetals[J]. Physical Review B, 1993, 48(17): 12511-12526. DOI:10.1103/PhysRevB.48.12511.
[4] CHEN S, KÜHNE P, STANISHEV V et al. On the anomalous optical conductivity dISPersion of electrically conducting polymers: Ultra-wide spectral range ellipsometry combined with a Drude-Lorentz model[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(15): 4350-4362.
[5] 陈篮,周岩. 膜厚度测量的椭偏仪法原理分析[J]. 大学物理实验, 1999, 12(3): 10-13.
[6] ZAPIEN J A, COLLINS R W, MESSIER R. Multichannel ellipsometer for real time spectroscopy of thin film deposition from 1.5 to 6.5 eV[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2000, 71(9): 3451-3460.
[7] DULTSEV F N, KOLOSOVSKY E A. Application of ellipsometry to control the plasmachemical synthesis of thin TiONx layers[J]. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics, 2015, 2015: 1-8.
[8] DULTSEV F N, KOLOSOVSKY E A. Application of ellipsometry to control the plasmachemical synthesis of thin TiONx layers[J]. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics, 2015, 2015: 1-8.
[9] YUAN M, YUAN L, HU Z et al. In Situ Spectroscopic Ellipsometry for Thermochromic CsPbI3 Phase Evolution Portfolio[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(14): 8008-8014.
[10] 焦杨景.椭偏仪在位表征电化学沉积的系统搭建.云南大学说是论文,2022.
[11] CANEPA M, MAIDECCHI G, TOCCAFONDI C et al. Spectroscopic ellipsometry of self assembLED monolayers: Interface effects. the case of phenyl selenide SAMs on gold[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(27): 11559-11565. DOI:10.1039/c3cp51304a.
[12] FUJIWARA H, KONDO M, MATSUDA A. Interface-layer formation in microcrystalline Si:H growth on ZnO substrates studied by real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry and infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 93(5): 2400-2409.
[13] FUJIWARA H, TOYOSHIMA Y, KONDO M et al. Interface-layer formation mechanism in (formula presented) thin-film growth studied by real-time spectroscopic ellipsometry and infrared spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 1999, 60(19): 13598-13604.
[14] LEE W K, KO J S. Kinetic model for the simulation of hen egg white lysozyme adsorption at solid/water interface[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2003, 20(3): 549-553.
[15] STAMATAKI K, PAPADAKIS V, EVEREST M A et al. Monitoring adsorption and sedimentation using evanescent-wave cavity ringdown ellipsometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(5): 1086-1093.
[16] VIEGAS D, FERNANDES E, QUEIRÓS R et al. Adapting Bobbert-Vlieger model to spectroscopic ellipsometry of gold nanoparticles with bio-organic shells[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017, 8(8): 3538.
[17] ARWIN H. Application of ellipsometry techniques to biological materials[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(9): 2589-2592.
[18] ZIMMER A, VEYS-RENAUX D, BROCH L et al. In situ spectroelectrochemical ellipsometry using super continuum white laser: Study of the anodization of magnesium alloy [J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 2019, 37(6): 062911.
[19] ZANGOOIE S, BJORKLUND R, ARWIN H. Water Interaction with Thermally Oxidized Porous Silicon Layers[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(11): 4027-4035.
[20] KYUNG Y B, LEE S, OH H et al. Determination of the optical functions of various liquids by rotating compensator multichannel spectroscopic ellipsometry[J]. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society, 2005, 26(6): 947-951.
[21] OGIEGLO W, VAN DER WERF H, TEMPELMAN K et al. Erratum to ― n-Hexane induced swelling of thin PDMS films under non-equilibrium nanofiltration permeation conditions, resolved by spectroscopic ellipsometry‖ [J. Membr. Sci. 431 (2013), 233-243][J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 437: 312..
[22] BROCH L, JOHANN L, STEIN N et al. Real time in situ ellipsometric and gravimetric monitoring for electrochemistry experiments[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2007, 78(6).
[23] BISIO F, PRATO M, BARBORINI E et al. Interaction of alkanethiols with nanoporous cluster-assembled Au films[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27(13): 8371-8376.
[24] 李广立. 氧化亚铜薄膜的制备及其光电性能研究[D]. 西南交通大学, 2016.
[25] 董金矿. 氧化亚铜薄膜的制备及其光催化性能的研究[D]. 安徽建筑大学, 2014.
[26] 张桢. 氧化亚铜薄膜的电化学制备及其光催化和光电性能的研究[D]. 上海交通大学材料科 学与工程学院, 2013.
[27] DISSERTATION M. Cellulose Derivative and Lanthanide Complex Thin Film Cellulose Derivative and Lanthanide Complex Thin Film[J]. 2017.
[28] NIE J, YU X, HU D et al. Preparation and Properties of Cu2O/TiO2 heterojunction Nanocomposite for Rhodamine B Degradation under visible light[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(27): 8118-8128.
[29] STRASSER P, GLIECH M, KUEHL S et al. Electrochemical processes on solid shaped nanoparticles with defined facets[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2018, 47(3): 715-735.
[30] XU Z, CHEN Y, ZHANG Z et al. Progress of research on underpotential deposition——I. Theory of underpotential deposition[J]. Wuli Huaxue Xuebao/ Acta Physico - Chimica Sinica, 2015, 31(7): 1219-1230.
[31] PANGAROV n. Thermodynamics of electrochemical phase formation and underpotential metal deposition[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1983, 28(6): 763-775.
[32] KAYASTH S. ELECTRODEPOSITION STUDIES OF RARE EARTHS[J]. Methods in Geochemistry and Geophysics, 1972, 6(C): 5-13.
[33] KONDO T, TAKAKUSAGI S, UOSAKI K. Stability of underpotentially deposited Ag layers on a Au(1 1 1) surface studied by surface X-ray scattering[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2009, 11(4): 804-807.
[34] GASPAROTTO L H S, BORISENKO N, BOCCHI N et al. In situ STM investigation of the lithium underpotential deposition on Au(111) in the air- and water-stable ionic liquid 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2009, 11(47): 11140-11145.
[35] SARABIA F J, CLIMENT V, FELIU J M. Underpotential deposition of Nickel on platinum single crystal electrodes[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 819(V): 391-400.
[36] BARD A J, FAULKNER L R, SWAIN E et al. Fundamentals and Applications[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2001.
[37] SCHWEINER F, MAIN J, FELDMAIER M et al. Impact of the valence band structure of Cu2O on excitonic spectra[J]. Physical Review B, 2016, 93(19): 1-16.
[38] XIONG L, HUANG S, YANG X et al. P-Type and n-type Cu2O semiconductor thin films: Controllable preparation by simple solvothermal method and photoelectrochemical properties[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(6): 2735-2739.
[39] KAZIMIERCZUK T, FRÖHLICH D, SCHEEL S et al. Giant Rydberg excitons in the copper oxide Cu2O[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7522): 343-347.
[40] RAEBIGER H, LANY S, ZUNGER A. Origins of the p-type nature and cation deficiency in Cu2 O and related materials[J]. Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2007, 76(4): 1-5.
[41] 舒云. Cu2O薄膜的电化学制备及其光电化学性能的研究[D]. 云南大学物理与天文学院,2019.
展示全部 